Abstract
The rapid advancement of intelligent driving technology has significantly accelerated the development of autonomous vehicles. Since 2023, deep learning has driven a new wave of innovation, leading to the emergence of Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models. By integrating visual perception, natural language processing, and action-based decision-making, VLA is poised to revolutionize autonomous driving. This article explores the breakthroughs in perception technology enabled by VLA, its intersection with artificial intelligence (AI), emerging market trends, and the challenges that must be addressed for widespread adoption. While VLA presents unprecedented opportunities, its integration into real-world driving environments requires overcoming substantial technical and regulatory barriers.
1. Introduction
The development of autonomous driving has reached a critical juncture, with deep learning and AI-powered models playing an increasingly central role in decision-making and perception. Traditional autonomous systems primarily rely on rule-based algorithms and sensor fusion techniques. However, these approaches often struggle with complex, dynamic environments, leading to inconsistencies in perception and decision-making.
The introduction of Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models marks a paradigm shift in intelligent driving. By incorporating vision-based perception, language-based reasoning, and action-oriented decision-making, VLA enables vehicles to process multimodal data more effectively, enhancing their adaptability and robustness. This article examines the potential of VLA in shaping the future of autonomous driving, focusing on its technical breakthroughs, applications, and challenges.
2. Breakthroughs in Perception Technology
Perception remains one of the most significant challenges in autonomous driving. Conventional models, which rely heavily on sensor-based inputs such as LiDAR, radar, and cameras, often struggle to interpret ambiguous or unforeseen scenarios. These limitations can result in misclassifications, slow response times, and failures in decision-making.
VLA represents a fundamental advancement in perception by integrating deep learning across multiple modalities. Unlike traditional approaches, which process visual inputs in isolation, VLA models incorporate linguistic reasoning and action-oriented frameworks to contextualize real-world scenarios. For example, when encountering a construction zone with obscured road signs, a VLA-enabled system can infer meaning from incomplete information, leveraging prior knowledge encoded through language models.
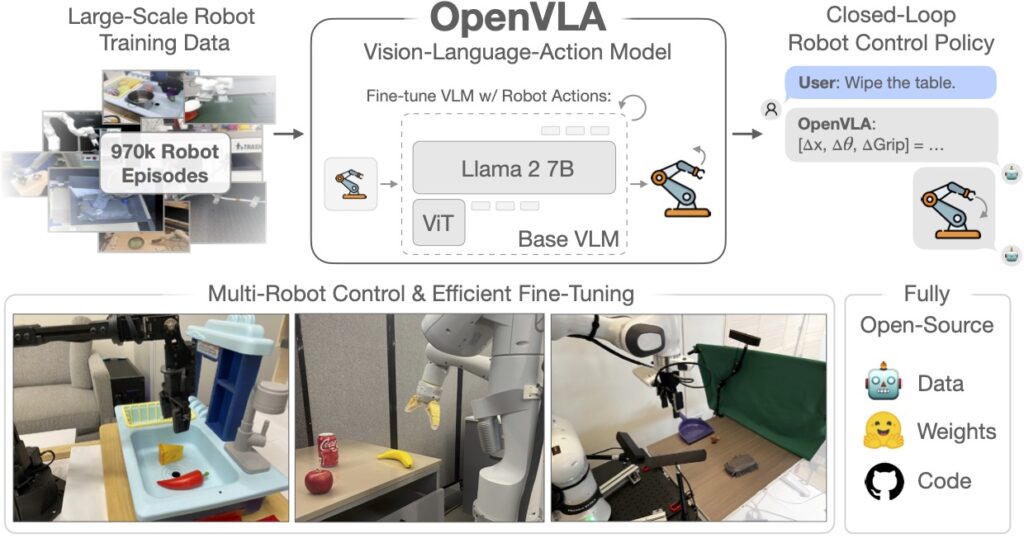
By employing self-supervised learning techniques, VLA models continuously refine their understanding of driving environments, reducing errors and improving generalizability. This capability makes VLA a promising solution for enhancing safety, efficiency, and real-time decision-making in autonomous systems.
3. The Intersection of AI and Autonomous Driving
VLA shares foundational principles with large language models (LLMs) such as OpenAI’s GPT and DeepMind’s multimodal AI architectures. These models excel in processing vast amounts of data, learning patterns, and generating context-aware responses. In the context of autonomous driving, VLA enables vehicles to reason beyond predefined rules, improving their ability to handle rare or unpredictable situations.
Industry experts describe VLA as the “second generation” of autonomous perception—capable of learning from vast datasets and adapting to diverse driving conditions. By incorporating multimodal learning, VLA-equipped vehicles can interpret road signs, predict pedestrian behavior, and optimize route planning more effectively than conventional systems. This advancement could significantly accelerate the transition from advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to fully autonomous driving.
4. Market Trends and Adoption Challenges
As VLA technology gains traction, market competition is intensifying. Leading companies, including Waymo, have introduced multimodal autonomous driving frameworks such as EMMA, underscoring the growing importance of integrated perception models. However, despite its potential, VLA adoption faces several challenges, including computational demands, integration with existing architectures, and regulatory scrutiny.
4.1 Core Challenges in Deployment
While VLA demonstrates strong technical capabilities, its implementation remains constrained by practical limitations. The integration of VLA into existing vehicle platforms requires significant computational power, often exceeding the capabilities of current embedded systems. Optimizing VLA models to function efficiently on hardware such as Nvidia’s Orin and Thor chips is critical to achieving real-time performance.
Additionally, regulatory frameworks for autonomous driving vary across jurisdictions, posing further challenges for widespread adoption. Ensuring that VLA models comply with safety standards, ethical considerations, and liability requirements will be essential for their commercial viability.
5. Conclusion: Potential and Challenges Ahead
VLA represents a transformative step in autonomous driving, bridging the gap between traditional perception models and next-generation AI-driven decision-making. By integrating vision, language, and action, VLA enhances the ability of autonomous systems to navigate complex environments with greater accuracy and adaptability.
However, significant hurdles remain. The scalability of VLA depends on advancements in hardware efficiency, regulatory approval, and real-world validation. While some industry leaders believe VLA could serve as the “missing piece” for achieving full autonomy, its long-term impact will ultimately be determined by its ability to integrate seamlessly with existing automotive ecosystems.
As research and development in VLA progress, the automotive industry must balance innovation with practical implementation. Companies that successfully navigate the technological and regulatory landscape will be well-positioned to lead the future of autonomous driving. While the road ahead presents challenges, the promise of VLA suggests that the next era of intelligent mobility is within reach.